electron domain and molecular geometry chart|Iba pa : iloilo Five Electron Domains. All molecules with 5 electron domains have trigonal bipyramidial electronic geometry. The central atom of these molecules must be in the third or . Now check out the best sex dice and get ready to roll: The Best Sex Dice Game Ever; Naughty Game; Lovehoney Oh! Foreplay Dice; Loopy; The Best Sex Dice Game ever. Pack it up everyone, this list is done. We’ve found ‘The Best Sex Dice Game Ever’. Apparently what that looks like is a game a bit like Yahtzee, except you’re rolling .
PH0 · molecular vs electron geometry chart
PH1 · molecular geometry chart pdf
PH2 · electron geometry vs molecular geometry
PH3 · electron domain geometry table
PH4 · electron and molecular geometry table
PH5 · domain geometry vs molecular geometry
PH6 · determine the electron geometry of ch3oh
PH7 · Iba pa
PH8 · 5 electron domain geometry
Seigyou Tensei - Legitimately Employed Reincarnation. 08. M onths passed. I spent more time with Zenith as she ballooned up, heavy with her second child. It was nice. Turns out, yeah, I had been neglecting her. I didn’t realize just how touchy-feely and physically needy she was until I started spending more time with her.Betsafe casino välkomstbonus. Hos Betsafe får du en välkomstbonus på 100% upp till 500 kr pluss 100 gratissnurr på Ancient Fortuneds Poseidon Megaways. Erbjudandet gäller för nya spelare som är minst 18 år och är bosatta i Sverige. Omsättningskravet på bonusen är 35x på casino, 6x på sport och bonusen är giltig 60 dagar.
electron domain and molecular geometry chart*******Five Electron Domains. All molecules with 5 electron domains have trigonal bipyramidial electronic geometry. The central atom of these molecules must be in the third or .
Geometry of Molecules Chart; Number of Electron Groups Electron-Group .There are five basic electron domain geometries. Linear The arrangement of 2 electron domains . – the two outer atoms are 180° from each other. Trigonal planar The .electron domain and molecular geometry chartTo use the VSEPR model to predict molecular geometries. To predict whether a molecule has a dipole moment. The Lewis electron-pair approach can be used to predict the .
Molecular Geometry Chart # of Electron Groups Number of Lone Pairs Electron Pair Arrangement Molecular Geometry Approximate Bond Angles 2 0 linear 180° 0 trigonal .The valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used to predict 3-D molecular geometry based on the number of valence shell electron bond pairs among .
Procedure: draw Lewis Structure, determine Steric Number (SN), Molecular Geometry and Hybridization SN = # of atoms bonded to the central atom plus # of lone pairs on the .
Electron domain is used in VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry of a molecule. The convention is to indicate the number of bonding electron .
Two regions of electron density around a central atom in a molecule form a linear geometry; three regions form a trigonal planar geometry; four regions form a .We can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing on only the number of electron pairs around the central atom, ignoring all other valence electrons .
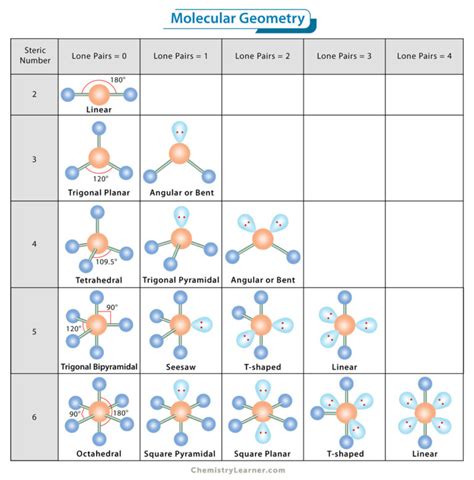
Molecular geometries (linear, trigonal, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral) are determined by the VSEPR theory. A table of geometries using the VSEPR theory can facilitate drawing and understanding molecules. The table of molecular geometries can be found in the first figure. The second figure serves as a visual aid for the table .Figure 5.2.2 5.2. 2: The BeF2 molecule adopts a linear structure in which the two bonds are as far apart as possible, on opposite sides of the Be atom. Figure 5.2.3 5.2. 3 illustrates this and other electron-pair .Molecular Geometry Chart # of Electron Groups Number of Lone Pairs Electron Pair Arrangement Molecular Geometry Approximate Bond Angles 2 0 linear 180° 0 trigonal planar 120° 1 3 bent <20° 0 tetrahedral 109.5° 1 trigonal pyramid 4 <109.5° (~107°) 2 bent <109.5°(~105°) 0 trigonal bipyramidal 9 0°,12 1 see-saw <9 0°,<12To predict the molecular geometry, follow these steps: 1. Draw the Lewis structure. 2. Count the electron domains, and determine whether they are bonding or non-bonding pairs. 3. Determine the electron domain geometry, molecular geometry, and bond angles. The chart below shows 3-dimensional representations of Lewis structures given .
The term electron geometry is the name of the electron pair/groups/domains on the central atom, whether they are bonding electrons or non-bonding electrons. Electron pairs are electrons that exist in pairs or bonds, as lone pairs or as a single unpaired electron. Because electrons are always in motion and their paths cannot be precisely .

Molecular geometry can be determined by the number of bonds that a particular molecule has. The main difference between electron geometry and molecular geometry is that electron geometry is found by taking both lone electron pairs and bonds in a molecule whereas molecular geometry is found using only the bonds present in .
Give an example of a molecule that would have the same molecular geometry as the electron geometry you’re studying (hint: pick a molecule with no lone pairs above the central atom). Unless otherwise stated, use the same-sized balloons for each electron domain. Take a set of two equivalent balloons and examine the geometry formed by . It is an arrangement of 2 electron domains. The outer atoms are at 180 o from eachother. The geometry lies in a straight line. 2. Trigonal Planar: It is an arrangement of 3 electron domains. At corners, three atoms lie in the equatorial plane. All atoms are at 120 o from each other. 3. Tetrahedral: It is an arrangement of 4 electron domains.
Procedure: draw Lewis Structure, determine Steric Number (SN), Molecular Geometry and Hybridization SN = # of atoms bonded to the central atom plus # of lone pairs on the central atom (SN = the effective number of electron pairs surrounding a central atom). Note: If one s and one p orbital hybridize, they form two sp hybrid orbitals. The number .Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional structure, or arrangement, of the atoms that make up a molecule. It is determined by the bonds between the atoms and any lone pairs of electrons that are present in the molecule. The geometry of a molecule can have a big impact on its chemical and physical properties, such as its reactivity and .
Iba paElectron Domain And Molecular Geometry. In chemistry and physics, the molecular geometry describes the geometric arrangement of the atoms that form a molecule. It is determined by the nature of the chemical bonds between the atoms. These constraints result in the molecule adopting a regular geometric form, like a polyhedron or a sphere.electron domain and molecular geometry chart Iba paElectron Domain And Molecular Geometry. In chemistry and physics, the molecular geometry describes the geometric arrangement of the atoms that form a molecule. It is determined by the nature of the chemical bonds between the atoms. These constraints result in the molecule adopting a regular geometric form, like a polyhedron or a sphere.The molecular geometry, or three-dimensional shape of a molecule or polyatomic ion, can be determined using valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (abbreviated VSEPR and pronounced “VES-per”) theory, in which the basic principle is valence electrons around a central atom stay as far apart as possible to. minimize the repulsions.Geometry of the water molecule with values for O-H bond length and for H-O-H bond angle between two bonds. Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule.It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters . If an atom has four electron domains, the electron domain geometry is tetrahedral, and the domains are 109.5 degrees from each other. Molecular Geometry Molecular geometry is based entirely on . Electron geometry teaches us about the arrangement of different electron groups. Molecular geometry, on the other hand, helps us understand the entire atom and its arrangement. It is the 3D arrangement of all the atoms in a particular molecule. So, when you compare them, you will note that atoms have different arrangements in .D The PF 5 molecule has five nuclei and no lone pairs of electrons, so its molecular geometry is trigonal bipyramidal. A The central atom, O, has six valence electrons, and each H atom contributes one valence electron. Subtracting one electron for the positive charge gives a total of eight valence electrons, so the Lewis electron structure is Geometrical isomers. For some molecules in the Table, we note that there is more than one possible shape that would satisfy the VSEPR rules. For example, the XeF 2 molecule has a steric number of five and a trigonal bipyramidal geometry. There are three possible stereoisomers: one in which the F atoms occupy axial sites, resulting in .
Desperate Amateurs - Watch ALL 348+ Desperate Amateurs XXX videos free at PORN.COM the world’s largest FREE porn tube. . PantyhoseSecret Party Hardcore PascalsSubSluts Passion-HD Perfect Gonzo PervMom Pervs On Patrol Peter North Piaceri69 PinkoHD PissVids PJGirls Playboy TV Porn Films 3D Porn For Women .
electron domain and molecular geometry chart|Iba pa